What is Two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication (also known as 2FA) is a method of confirming a user's claimed identity by utilizing a combination of two different components. Two-factor authentication works as an extra step in the process, a second security layer, that will reconfirm your identity. Its purpose is to make attackers’ life harder and reduce fraud risks. If you already follow basic password security measures, two-factor authentication will make it more difficult for cybercriminals to breach your account.
What is Google Authenticator?
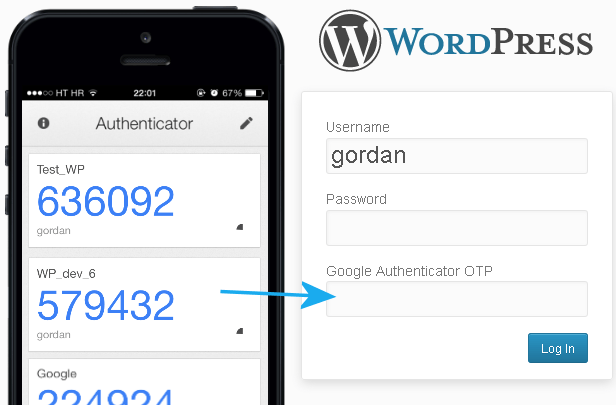
Google Authenticator is a software token that implements two-step verification services using the Time-based One-time Password Algorithm (TOTP) and HMAC-based One-time Password Algorithm (HOTP), for authenticating users of mobile applications by Google. Authenticator provides a six- to an eight-digit one-time password which users must provide in addition to their username and password to log into sites. The Authenticator can also generate codes for third-party applications, such as password managers or file hosting services.
ASK US ANYTHING WORDPRESS RELATED: We can offer you confidently, SEVERAL OPTIONS to choose which one suits your needs better.
How does Google Two-factor authentication work?
The most common form of two-factor authentication when logging into an account is the process of entering your username, then your password and then your generated code from your phone's Google Authenticator. Google Authenticator codes expire quickly, usually after 30 or 60 seconds. An authentication app still works when you don't have cell service.
Why should you activate Two-Factor Authentication?
The problem with the standard authentication model is: it relies only on something everybody knows (your username or email) and that something is often easily guessed, cracked, or otherwise compromised. While a username may seem like "something you are," it is just a word, so it is actually "something everybody knows" - which is generally not protected or kept secret, so it is a non-factor. That leaves the password.
Passwords on their own aren’t as infallible as we need them to be. Cyber attackers have the power to test billions of passwords combinations in a few minutes. What’s even worse, 65% of people use the same password everywhere. Many people also rely on the same username and password to protect all of their various accounts, thus making that one pair the control-all entity to the entire digital life.
Answers to security questions are also easy to find out, especially now that we are willingly sharing all the details about our lives on social networks and blogs. Anyone that interacts with us on a daily basis can find out the answers to common security questions, such as the graduation year, the city that you grew up in or our first pet’s name.
This is where two-factor authentication comes in handy. It will offer you an extra layer of protection, besides passwords. This will drastically reduce cybercriminals chances to do harm.
Ideas implemented from constrained points of view (biased developers, designers, sysadmins) will NOT BENEFIT YOUR online strategies, harming your long-term competitiveness.
We're passionate about helping you grow and make your impact
Continue being informed
Monthly vulnerability reports about WordPress and WooCommerce, plugins, themes.
Weekly inspiration, news and occasional with hand-picked deals. Unsubscribe anytime.
















