11 XSS - Cross-Site Scripting - WordPress Security DEC, 2020
Be informed about the latest Cross-Site Scripting, identified and reported publicly in December 2020. As these WordPress Security vulnerabilities have a severe negative impact for any website, consider a security AUDIT. The following PLUGINS made headlines just last month.
- LiteSpeed Cache < 3.6.1 - Authenticated Stored Cross-Site Scripting
- LiteSpeed Cache for WordPress (LSCWP) is an all-in-one site acceleration plugin, featuring an exclusive server-level cache and a collection of optimisation features. Active installations: 1+ million
- WP-PostRatings < 1.86.1 - Authenticated Stored Cross-Site Scripting
- If you want to embed other post ratings use [ratings id="1"], where 1 is the ID of the post/page ratings that you want to display. Active installations: 80,000+
- Gallery Plugin for WordPress – Envira Photo Gallery < 1.8.3.3 - Authenticated Stored Cross-Site Scripting
- We believe that you shouldn’t have to hire a developer to create a WordPress gallery. That’s why we built Envira, a drag & drop photo gallery plugin that’s both EASY, FAST and POWERFUL. Active installations: 100,000+
- Simple Social Media Share Buttons – Social Sharing for Everyone < 3.2.1 - Unauthenticated Reflected Cross-Site Scripting
- Simple Social Media Share Buttons – Social Sharing for Everyone < 3.2.0 - Reflected Cross-Site Scripting
- Simple Social Buttons adds ( with lots of options like Sidebar, inline, above and below the posts content, on photos, popups, fly ins ) an advanced set of social media sharing buttons to your WordPress sites, such as: Facebook, WhatsApp, Viber, Twitter, Reddit, LinkedIn and Pinterest. Active installations: 40,000+
- Limit Login Attempts Reloaded < 2.16.0 - Authenticated Reflected Cross-Site Scripting
- Limit the number of login attempts that are possible through the normal login as well as XMLRPC, Woocommerce and custom login pages. WordPress by default allows unlimited login attempts. This can lead to passwords being easily cracked via brute-force. Active installations: 1+ million
- Advanced Classifieds & Directory Pro < 1.3.46 - Authenticated Self-Reflected Cross-Site Scripting
- Advanced Classifieds & Directory Pro < 1.3.46 - Authenticated Reflected Cross-Site Scripting
- ACADP is a professional, powerful, flexible, high quality directory plugin, you can create any kind of directory site. Active installations: 4,000+
- Page Builder: PageLayer – Drag and Drop website builder < 1.3.5 - Multiple Reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Pagelayer is a WordPress page builder plugin. Its very easy to use and very light on the browser. Pagelayer works with any WordPress theme. Pagelayer is a real time editor and you can create beautiful web pages and web sites in a few minutes ! You dont need any programming knowledge when using Pagelayer. Pagelayer comes with top-notch features with a great UX and simple UI. Active installations: 200,000+
- Themify Portfolio Post < 1.1.6 - Authenticated Stored Cross-Site Scripting
- Themify Portfolio Posts is a simple plugin that allows you to showcase your projects info in a clean layout. Minimal and sleek, you can click on each image of your gallery portfolio and opt to show further details such as the project type, client name, and commission date – or edit each heading and name your own. Active installations: 50,000+
- DiveBook <= 1.1.4 - Unauthenticated Reflected XSS
- This plugin has been closed as of December 9, 2020 and is not available for download. This closure is temporary, pending a full review.
Protect your WordPress: BEFORE IT'S TOO LATE! You will also protect your customers, your reputation and your online business!
BRIEF: Cross-site scripting is a type of security vulnerability typically found in web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting vulnerability may be used by attackers to bypass access controls such as the same-origin policy.
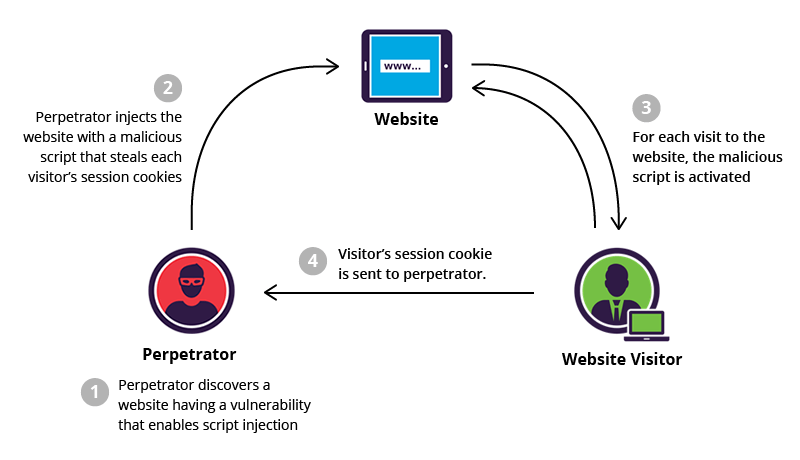
What is Cross-Site Scripting?
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks are a type of injection, in which malicious scripts are injected into otherwise benign and trusted websites. XSS attacks occur when an attacker uses a web application to send malicious code, generally in the form of a browser side script, to a different end user. Flaws that allow these attacks to succeed are quite widespread and occur anywhere a web application uses input from a user within the output it generates without validating or encoding it.
An attacker can use XSS to send a malicious script to an unsuspecting user. The end user’s browser has no way to know that the script should not be trusted, and will execute the script. Because it thinks the script came from a trusted source, the malicious script can access any cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information retained by the browser and used with that site. These scripts can even rewrite the content of the HTML page.
What is the impact of a CSRF attack?
The actual impact of an XSS attack generally depends on the nature of the application, its functionality and data, and the status of the compromised user. For example:
- In a simple public application, where all users are anonymous and all information is public, the impact will often be minimal. Nothing else to steal.
- In an application holding sensitive or private/personal data, such as banking transactions, emails, or healthcare records, the impact will usually be serious.
- If the compromised user has elevated privileges within the application, then the impact will generally be critical, allowing the attacker to take full control of the vulnerable application and compromise all users, owners and their data.
What kind of XSS attacks are exploited?
- Reflected XSS, where the malicious script comes from the current HTTP request.
- Stored XSS, where the malicious script comes from the website's database.
- DOM-based XSS, where the vulnerability exists in client-side code rather than server-side code.
Get Healthy, Stay Healthy: A healthier online business starts today and it begins with you!
Do you suspect any Cross-Site Scripting within your WordPress? Contact us today for a free scan!
We’re passionate about helping you grow and make your impact
Continue being informed
Monthly vulnerability reports about WordPress and WooCommerce, plugins, themes.
Weekly inspiration, news and occasional with hand-picked deals. Unsubscribe anytime.